n the realm of modern medicine, a revolutionary field is gaining momentum, offering hope to patients with previously untreatable conditions and injuries. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine are transforming the way we approach healthcare by harnessing the power of biology, materials science, and engineering to create new tissues and organs for transplantation and repair.
The Essence of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
Tissue engineering involves the creation of functional tissues or organs by combining cells, biocompatible materials, and biochemical cues. This innovative approach holds immense potential for a wide range of applications, from replacing damaged heart tissue after a heart attack to restoring mobility for individuals with spinal cord injuries.
Stem Cells as the Building Blocks
At the heart of tissue engineering lies the use of stem cells, the body’s natural repair system. Stem cells have the remarkable ability to transform into various cell types, making them ideal for generating the diverse cell populations required for tissue regeneration. Researchers are constantly exploring new ways to harness the potential of stem cells, whether derived from embryonic sources or induced from a patient’s own cells through reprogramming techniques like iPSCs (induced pluripotent stem cells).
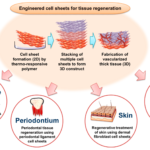
Scaffolds and Bioengineering Materials
Creating the right environment for cells to grow and differentiate is crucial in tissue engineering. Scaffolds and bioengineering materials provide the necessary physical support and biochemical cues. These materials must be biocompatible, biodegradable, and able to mimic the extracellular matrix—the natural environment surrounding cells in the body. Researchers are continually refining these materials to enhance their properties, making them more suitable for various tissue types.
Clinical Applications and Success Stories
Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine have already made significant strides in clinical applications. Some notable success stories include:
- Skin Regeneration: Researchers have developed artificial skin grafts to treat burn victims, offering quicker and more effective healing.
- Cartilage Repair: New approaches to cartilage regeneration are providing hope for those suffering from joint conditions like osteoarthritis.
- Organ Transplants: Although fully functional organs are still a work in progress, there have been successful transplants of engineered tracheas and bladders.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the potential of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine is immense, several challenges and ethical considerations must be addressed. These include issues related to tissue rejection, the development of complex organs, and the responsible use of emerging technologies like gene editing.
The Road Ahead
Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine represent a beacon of hope for countless individuals facing debilitating injuries and diseases. As research continues to advance, we can anticipate even more groundbreaking developments in the field, bringing us closer to a future where damaged organs can be replaced, and the quality of life for many can be significantly improved.
In conclusion, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine offer a glimpse into the future of healthcare—a future where the boundaries of what’s medically possible are continually pushed, and where the human body’s incredible regenerative potential is harnessed to heal, repair, and rejuvenate. The journey ahead is exciting, and the prospects are nothing short of extraordinary.